EPR compliance, made easy
Comply with DENR regulations and elevate your brand through traceable plastic offsets that uplift local communities.

By 2028, businesses in the Philippines must demonstrate recovery and diversion of 80% of their plastic packaging footprint
A DENR-approved partner for your EPR success
Plastic Bank’s EPR solution simplifies compliance while delivering real impact.
We provide:

DENR-approved PRO services
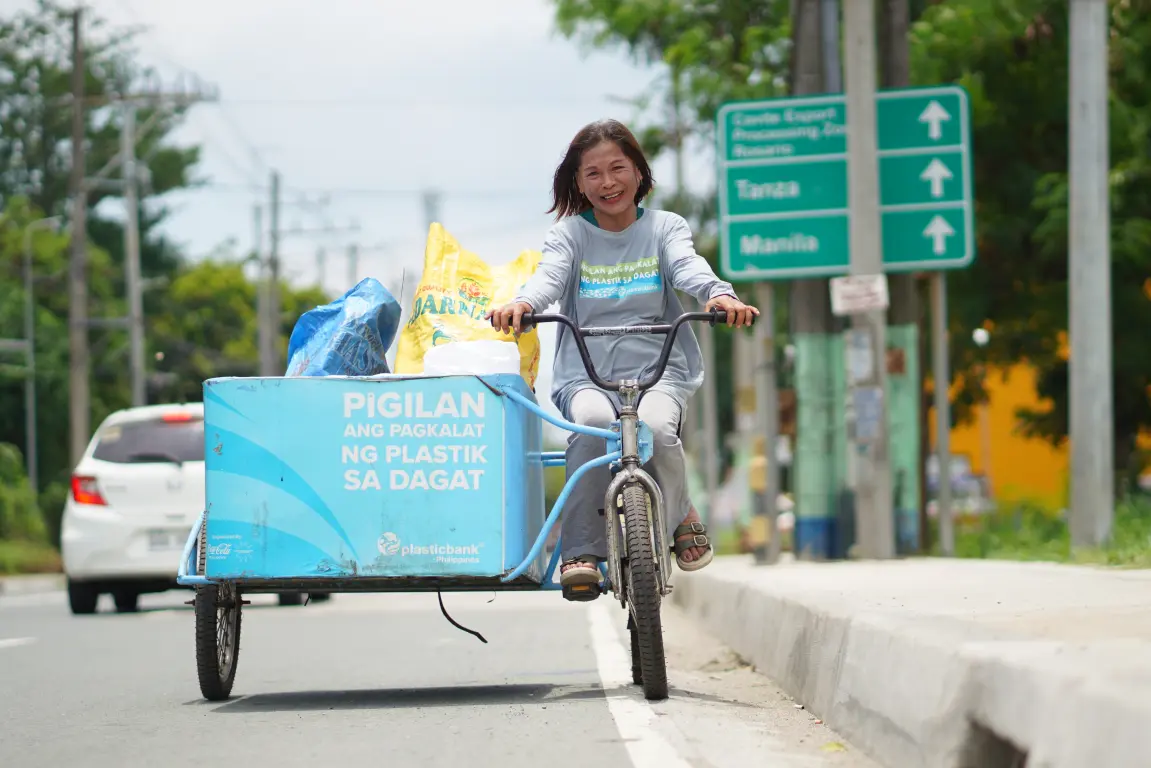

Over 260 collection branches across the Philippines
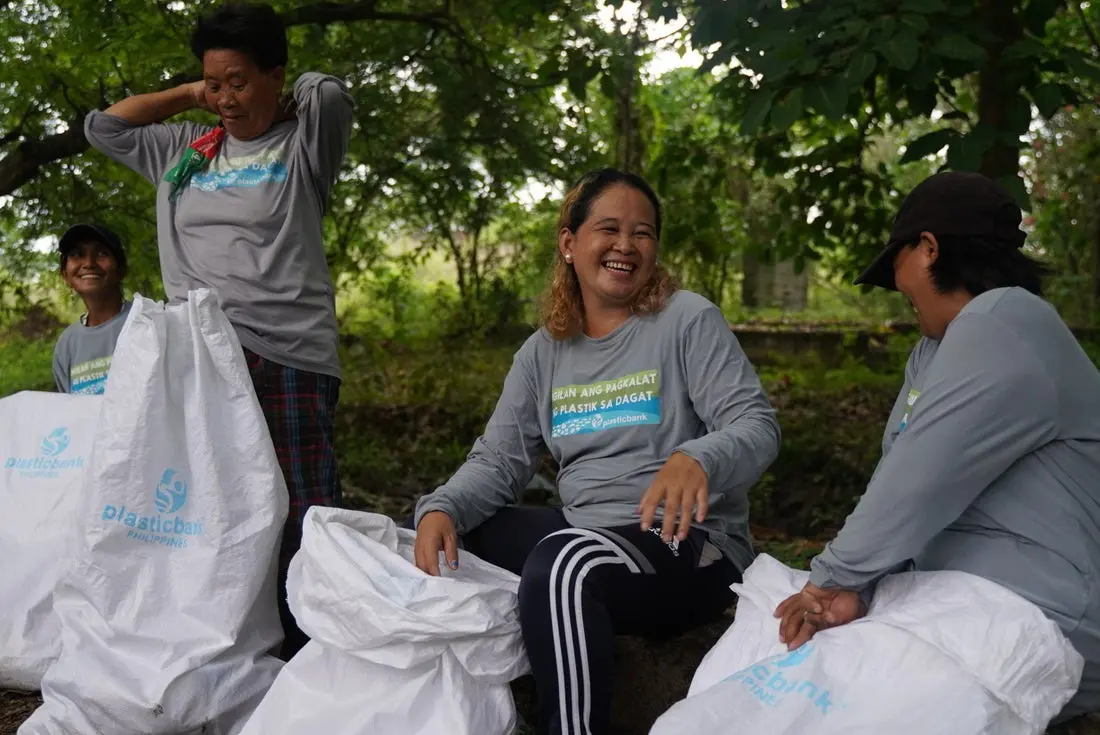

A trained network of 22,000+ plastic collection members
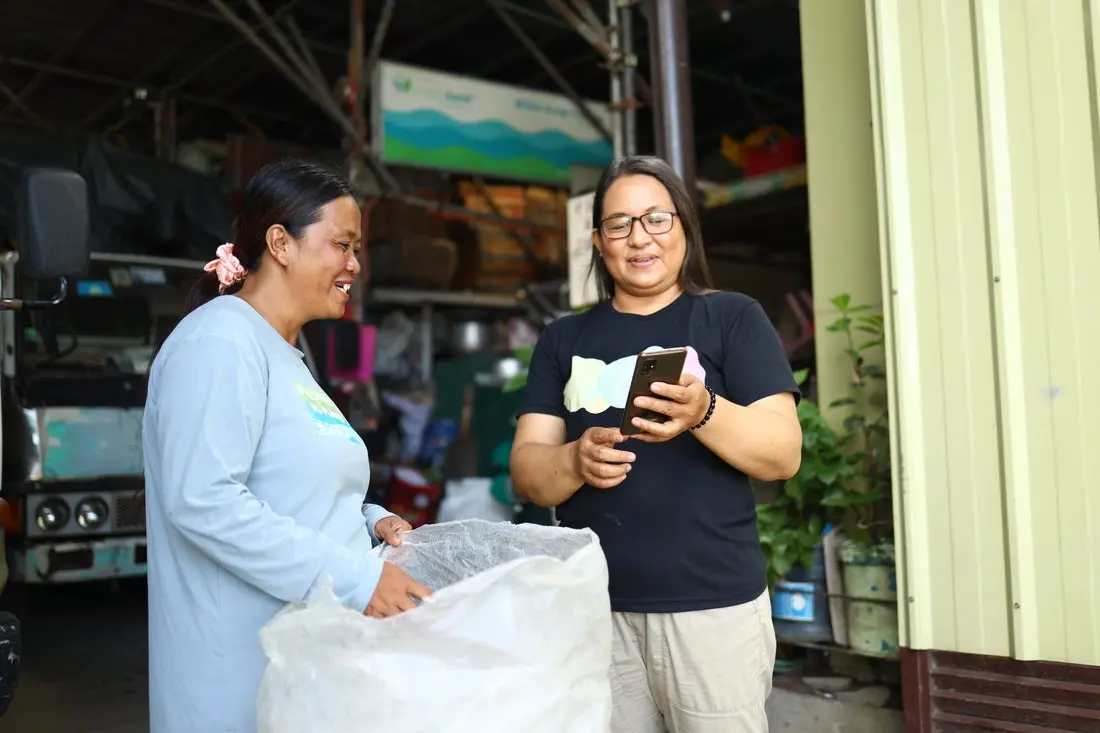

Full traceability and audit-ready documentation
Trusted by leading brands






























The cost of doing it alone
Only 900 out of 2,000+ obliged enterprises are
registered with DENR. Many are struggling with:
Setting up independent recovery systems
Coordinating multiple third-party vendors
Falling short on traceability and audit readiness
Facing steep penalties for non-compliance
You don’t have to navigate it alone.
Your EPR compliance, handled
Avoid the penalties, confusion, and complexity.
Partner with a proven, government-approved solution—and create meaningful environmental and social impact along the way.
For general enquiries please use our contact page.
Skip the Complexity.
Gain Compliance and Credibility.
What you avoid
- Building costly infrastructure
- Managing multiple vendors
- Struggling with reporting and audits
What you get
- Verified plastic offsets recognized by DENR
- Plastic offset certification badges
- ESG-ready reports and traceable documentation
How it works

Calculate

Offset

Verify

Report
-
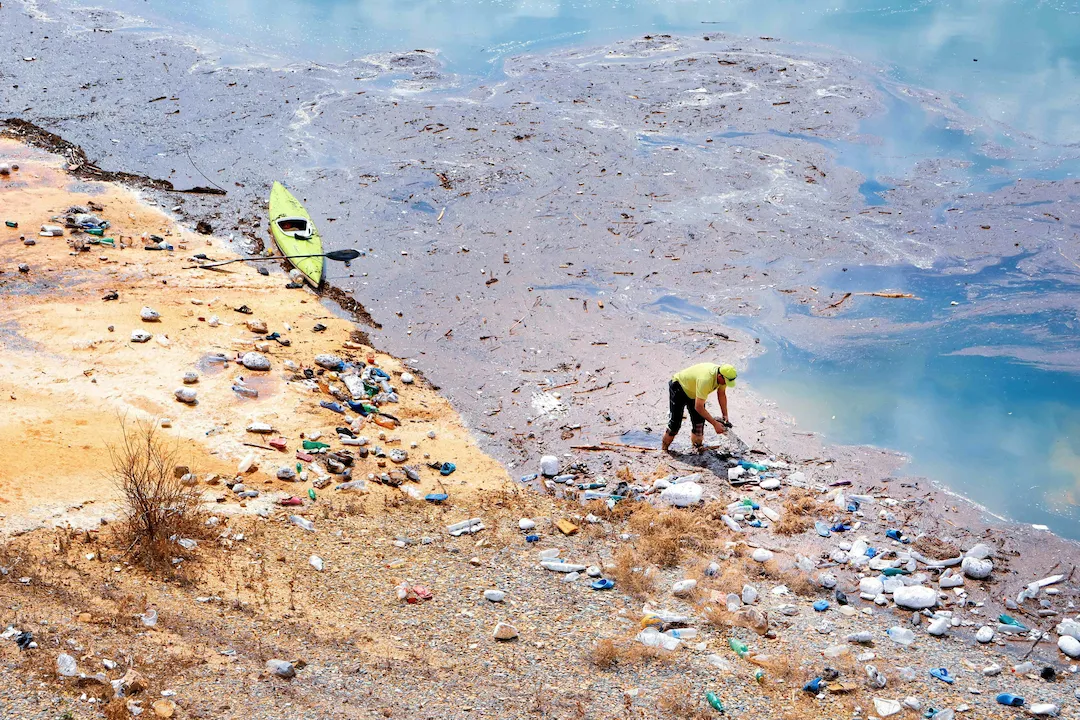

The missing link in EPR? Community-based plastic collection
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for plastic waste is gaining momentum around the world as governments and businesses try to address the growing plastic pollution problem.…
-

Are you an obliged enterprise under the EPR law in the Philippines?
If your company sells or imports products into the Philippines, you may already fall under the EPR Law Philippines, also known as Republic Act No.…
-
The power of technology in EPR compliance tracking and reporting
EPR compliance tracking has become essential for companies operating in the Philippines under Republic Act 11898, the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) law of 2022. As…
-

Building sustainability with EPR, the Plastic Bank way
Imagine transforming your brand’s commitment to sustainability into a powerful movement that doesn’t just fulfill compliance—it fuels prosperity.
-

Embracing extended producer responsibility (EPR) for shared prosperity: a holistic approach to reducing plastic pollution
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is more than a regulatory checkbox—it’s a strategic framework that holds producers accountable for the full life cycle of the products…
Have Questions? We’re Here to Help
What is EPR law in the Philippines?
The Philippine EPR Act of 2022 mandates Obligated Enterprises to recover their plastic packaging waste responsibly. This involves redesigning plastic packaging to enhance reusability, recovery, or recyclability. Additionally, it includes measures such as offsetting, redemption, or buy-back of plastic waste, as well as contributing to the collection and transportation of recovered plastic waste to appropriate recycling sites. By holding manufacturers accountable, the law aims to reduce plastic pollution and promote a circular economy.
These are its key objectives:
- Institutionalize Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) mechanisms to minimize plastic waste through improving waste management focusing on recovery and recycling and extending the life cycle of a product for full circularity
- Encourage public-private cooperation in waste management at national and local levels
- Promote education and awareness on sustainable practices and ecological responsibility
What are the obligations of EPR in the Philippines?
The Philippine EPR Act of 2022 mandates producers to recover their product plastic packaging waste, promoting eco-friendly practices such as recycling to facilitate plastic recovery and foster a circular economy. It aims to minimize environmental harm by holding Obliged Enterprises responsible for the entire lifecycle of their goods, from production to disposal.
Obliged Enterprises (OE) must comply with the following:
- Submit EPR Program: Each OE must design and register an EPR program with the DENR. This should include plans to reduce, phase out, or offset plastic packaging, enhance recyclability, or achieve plastic neutrality.
- Undergo Third-Party Audit: Programs and OEs must be audited annually and submitted to the DENR. For the OEs, audits must be also conducted internally within their organization to validate their plastic footprint, either in totality or for the given compliance year
- Ensure Traceability: The system must trace plastics from where the plastic waste was collected as well as its next of life, and verified via a certificate issued by the Waste Diverter or Producer Responsibility Organization. The Certificate must also be notarized in accordance with the EPR Law
- Offset plastic based on these targets:
| Compliance Year | Required Offset |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 20% of 2022 footprint |
| 2024 | 40% of 2023 footprint |
| 2025 | 50% of 2024 footprint |
| 2026 | 60% of 2025 footprint |
| 2027 | 70% of 2026 footprint |
| 2028 onwards | 80% of previous year’s footprint |
What are the different ways to comply with EPR requirements?
A. Product Redesign and Reduction:
- Minimize the use of non-environmentally friendly materials through redesign.
- Incorporate recycled content into products.
- Reduce overall plastic use.
- Implement information, education, and communication (IEC) campaigns.
- Improve product labeling for better consumer awareness.
B. Waste Recovery Programs designed to prevent plastic waste from leaking into the environment. These may include:
- Buy-back, redemption, or offsetting schemes to recover post-consumer plastic waste.
- Reintegration of recovered waste into value chains through recycling or other sustainable methods.
- Clean-up activities targeting coastal areas, public roads, waterways, and other affected locations.
- Collaborations with LGUs, communities, and the informal waste sector to enhance plastic recovery efforts.
- Proper transport of recovered waste to certified recycling, composting, or disposal facilities within the country.
- Development of waste diversion infrastructure, including recycling, composting, thermal treatment, and other environmentally sound facilities.
How does Plastic Bank help with EPR?
Plastic Bank enables obliged enterprises to meet their EPR obligations through plastic waste recovery and diversion programs designed to prevent waste from leaking into the environment. Our model combines community impact, traceability, and measurable plastic diversion so companies can comply with RA 11898 with confidence:
Here’s how we support EPR compliance:
a. Waste Recovery Schemes (Buy-Back, Redemption, and Offsetting)
Plastic Bank operates community-based collection systems where collectors can exchange plastic waste for financial incentives. This approach helps companies recover measurable volumes of post-consumer plastic to offset their footprint and meet mandated recovery targets.
b. Diversion of Recovered Waste into Circular Value Chains
Collected materials are processed into a certified, high-quality recycled material that is sold to companies to be reintegrated into new products and packaging, which helps reduce the demand for virgin plastic.
Transportation of Recovered Waste to Accredited Facilities
We facilitate the safe and compliant transport of recovered plastic to authorized recycling facilities to ensure responsible waste handling.
What penalties are enforced for EPR violations in the Philippines?
Obligated enterprises (OEs) violating the EPR Act of 2022 would be fined P5 million to P20 million (USD 90,000 – 181,000) and face the automatic suspension of their business permits on the third offense.
Which enterprises or businesses must adhere to EPR regulations in the Philippines?
Obliged Enterprises are large enterprises that generate plastic packaging waste involved in manufacturing, importing, selling, distributing, and using products covered by EPR laws must comply in the Philippines with at least 100,000,000 Million Pesos in assets.
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are not mandated, but encouraged to participate voluntarily.
How much plastic recovery does the Philippines EPR Act of 2022 require?
By the end of 2023, companies need to demonstrate recovery and diversion of 20 percent of their 2022 plastic packaging footprint; 40 percent by 2024, with 10 percent annual increase up to 80 percent by 2028 and onwards.
What advantages does Plastic Bank offer for meeting EPR requirements?
- Verified plastic collection and recycling solution
Its blockchain platform allows tracking the plastic collection and recycling journey from collection to processing, ensuring verified data for audits and reports. - Social impact for informal waste collection communities that collect plastic for recycling.
- Large, consistent collection capacity
With a monthly collection capacity of 500 to 1,000 tons, it can ensure the fulfilment of large plastic recovery requirements.
What services does Plastic Bank offer to support EPR compliance?
Plastic Bank supports Obliged Enterprises in achieving EPR Compliance as a Waste Diverter and as a Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO).
As a waste diverter, Plastic Bank operates programs to collect and recycle post-consumer products and packaging.
As a Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO), Plastic Bank:
- Tracks the volume of waste recovered and provides companies with verified collection to comply with government-mandated recovery targets
- Manages partnerships by building networks with collector communities and recycling facilities
- Provides auditable reporting and documentation on the entire waste recovery process to support regulatory submissions
- Educates and engages stakeholders through awareness campaigns, provides training, and engages communities, brands and LGs to strengthen overall waste management systems.
How does EPR compliance help business growth?
Under the law, OEs may receive awards (monetary or otherwise) for outstanding initiatives in reuse, recycling, or reduction.
OEs and MSMEs may apply for tax and fiscal incentives under the National Internal Revenue Code, pending alignment with the Strategic Investment Priority Plan. Final guidelines are under development by the DENR and Department of Finance.
EPR compliance drives business growth by bolstering brand reputation, cutting waste management expenses, spurring product innovation, and ensuring legal adherence. This attracts eco-conscious consumers and investors, while mitigating environmental liabilities, fostering resource efficiency, and maintaining compliance, thereby nurturing sustainable business expansion.






